Thu, Jan 23, 2025
[Archive]
Volume 21, Issue 1 (March - Special Issue 2024)
IJMSE 2024, 21(1): 56-63 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Kulkarni Y, Pawar N, Erandole N, Mulani M, Shikalgar M, Banne S, et al . CuO (Copper Oxide) Thin Films by Successive Ionic Layer Adsorption and Reaction (SILAR): A Sustainable Approach for Solar-Driven Methylene Blue (MB) Degradation. IJMSE 2024; 21 (1) :56-63
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-3539-en.html
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-3539-en.html
Yugen Kulkarni 
 , Niketa Pawar
, Niketa Pawar 
 , Namrata Erandole
, Namrata Erandole 
 , Muskan Mulani
, Muskan Mulani 
 , Mujjamil Shikalgar
, Mujjamil Shikalgar 
 , Swapnil Banne
, Swapnil Banne 
 , Dipali Potdar
, Dipali Potdar 
 , Ravindra Mane
, Ravindra Mane 
 , Smita Mahajan
, Smita Mahajan 
 , Prashant Chikode
, Prashant Chikode 


 , Niketa Pawar
, Niketa Pawar 
 , Namrata Erandole
, Namrata Erandole 
 , Muskan Mulani
, Muskan Mulani 
 , Mujjamil Shikalgar
, Mujjamil Shikalgar 
 , Swapnil Banne
, Swapnil Banne 
 , Dipali Potdar
, Dipali Potdar 
 , Ravindra Mane
, Ravindra Mane 
 , Smita Mahajan
, Smita Mahajan 
 , Prashant Chikode
, Prashant Chikode 

Abstract: (7247 Views)
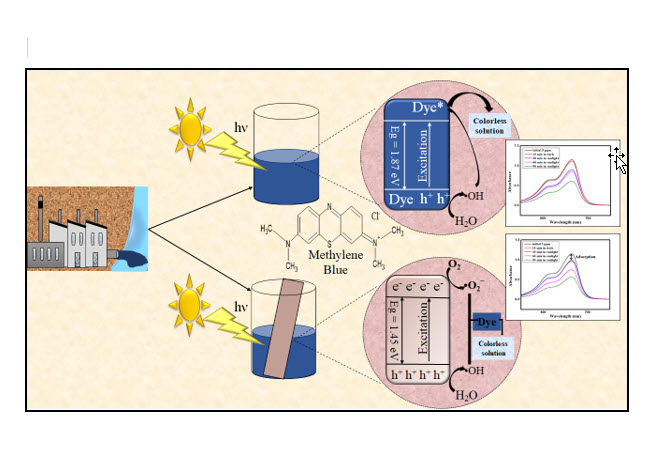
The paper investigates the solar photodegradation of Methylene Blue dye using copper oxide (CuO) thin films synthesized by the Successive Ionic Layer Adsorption and Reaction (SILAR) method. The structural, morphological, and optical characteristics of the CuO thin films have been investigated by employing a variety of methods, such as Fourier transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, UV-Vis spectroscopy, Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The outcomes showed that CuO thin films with excellent surface shape and a highly crystalline nature had been successfully deposited. Methylene Blue was subjected to solar radiation during its photodegradation process, and the outcomes showed a significant decrease in the dye's concentration over time. To maximize the photo degradation process, the effects of other experimental factors were also assessed, such as the starting concentration of MB, the quantity of CuO thin film, number of SILAR cycles and the pH of the solution. Good photocatalytic activity is demonstrated by CuO thin films produced using the SILAR approach in the solar photodegradation of methylene blue. The development of affordable and ecologically friendly wastewater treatment technology that can use sun energy to break down persistent organic contaminants is affected by these findings.
Type of Study: Research Paper |
Subject:
Other subjects
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |